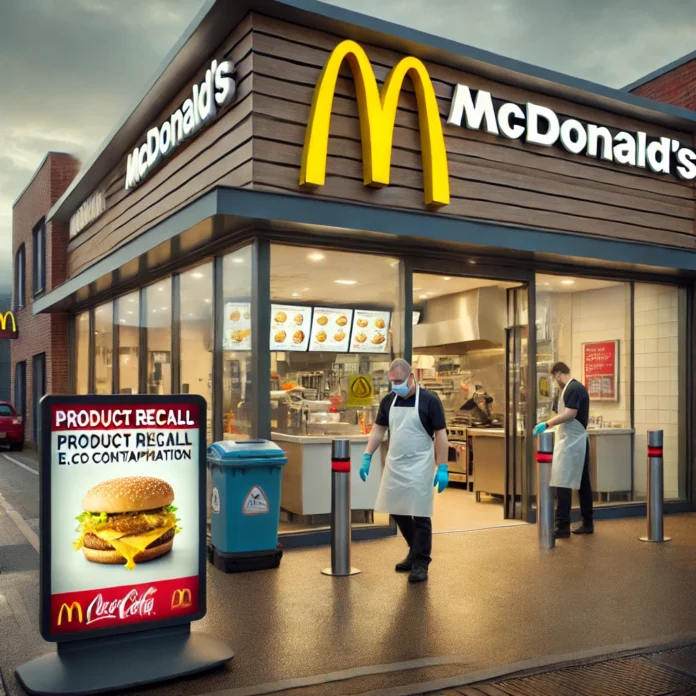
McDonald’s E. coli Crisis: How It Unfolded
McDonald’s, the global fast-food leader, is dealing with a significant public health and business crisis following an E. coli outbreak traced to its popular Quarter Pounder burgers. Since the initial report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the outbreak has spread across 13 states, affecting over 75 individuals and causing at least one death. This unfortunate situation shines a light on the ongoing risks associated with foodborne illnesses in the restaurant industry and raises questions about how McDonald’s, alongside health authorities, will address it.
This outbreak links back to slivered onions in Quarter Pounders, produced by Taylor Farms, which recently issued a recall on four raw onion products after finding E. coli contamination. Given the scale and reach of McDonald’s, this incident has rippled through the company’s vast supply chain and customer base, with implications for both public health and investor confidence.
Read: Understanding E. coli: Causes, Risks, and Prevention in the Food Industry
Financial Impact on McDonald’s: Market Reactions
The financial repercussions for McDonald’s are already visible. Shares in the company have dropped by 7% since the CDC’s advisory notice. For a company known for its strict quality controls, such a drastic drop highlights investor concerns over both consumer confidence and potential lost revenue. Even more worrying for stakeholders, as the number of cases continues to rise, McDonald’s is forced to halt sales of its Quarter Pounder burgers in affected areas and suspend the distribution of slivered onions across a substantial portion of its U.S. restaurants.
While McDonald’s has not yet disclosed how this incident may affect quarterly earnings, the timing is unfortunate, as its Q3 financial report is due in just a few days. With inflation concerns and increasing costs for fast food, this E. coli incident has heightened scrutiny from investors looking for clear assurances of the company’s crisis management and preventive measures.
Steps Taken: McDonald’s Response to the Outbreak
In response, McDonald’s has pulled affected Quarter Pounder burgers from the impacted regions and removed slivered onions from its supply chain in the specified areas. The CDC and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are working closely with McDonald’s to trace the contamination and prevent any further spread. However, investigations like this can last weeks or even months, making it challenging for McDonald’s to restore confidence quickly.
President of McDonald’s USA, Joe Erlinger, has publicly addressed the issue, sharing steps McDonald’s is taking to maintain food safety. Additionally, Erlinger appeared on NBC’s “TODAY” show to assure customers of the safety of the chain’s products.
The Contamination Source: Focus on Onions and Beef
Health authorities are focusing on both slivered onions and the beef patties in the Quarter Pounder to identify the source of E. coli. E. coli bacteria can spread through contaminated food, water, or direct contact with an infected person or surface. While the CDC suspects onions, beef remains a plausible source of contamination due to possible cross-contamination during the preparation process. However, McDonald’s uses a high-temperature cooking method that should theoretically kill E. coli in ground beef, leading investigators to scrutinize preparation processes.
Dr. Thomas Jaenisch, an epidemiology professor, emphasized the possibility of cross-contamination during burger preparation as another angle to consider in preventing further cases. Investigators are likely to examine food preparation protocols, distribution channels, and sanitation practices to identify the root cause.
Food Safety Lessons: Recent Outbreaks and Their Impact on Fast-Food Chains
For McDonald’s, the stakes in addressing this outbreak are higher than just the immediate financial impact. The company’s reputation, shaped over decades of operations, is under scrutiny. Past outbreaks at other chains offer insight into the potential impact on consumer trust and financial stability.
- Wendy’s E. coli Incident: Wendy’s experienced an E. coli outbreak in 2022 that affected over 100 people but had limited long-term impact. The quick response helped mitigate any serious damage to the brand.
- Chipotle’s Crisis: In contrast, Chipotle suffered significantly from multiple outbreaks between 2015 and 2016, which affected customer trust and brand image, resulting in a years-long struggle to regain its reputation. This example serves as a cautionary tale for McDonald’s, emphasizing the importance of transparency and rigorous food safety measures.
- Jack in the Box Tragedy: One of the most severe incidents occurred at Jack in the Box in the early 1990s, where an E. coli outbreak resulted in the deaths of four children and led to drastic changes in the company’s practices and reputation. This outbreak stands as a stark reminder of the potential consequences of foodborne illnesses in the restaurant industry.
These examples illustrate the importance of transparent, immediate responses, as well as the need to reassure both the public and shareholders of ongoing safety efforts.
Maintaining Customer Trust: Strategies for Reassurance
Restoring customer trust will be critical for McDonald’s to minimize potential long-term damage. To reassure the public, McDonald’s is taking visible steps, including temporarily pulling the affected items and emphasizing food safety protocols across its restaurants. Additionally, company leadership is engaging in public communications and interviews to address concerns directly.
Experts like Dr. Darin Detwiler, a professor of food policy, recommend that McDonald’s adopt a proactive approach by increasing sanitation procedures and testing ingredients even in unaffected regions. This type of action could prevent future outbreaks while also demonstrating a commitment to rigorous safety measures. Food safety attorney Bill Marler suggests McDonald’s should support any affected individuals, perhaps even covering medical expenses, similar to the approach Jack in the Box took years ago.
The Future of McDonald’s and the Impact on Fast-Food Safety Standards
For fast-food giants like McDonald’s, the E. coli outbreak underscores the complexities and vulnerabilities in even the most established supply chains. Food safety in large operations requires continual refinement of protocols, especially as foodborne pathogens become more prevalent. By transparently addressing this incident, McDonald’s has the opportunity to reinforce its commitment to consumer safety, both for immediate reassurance and to set an industry example.
While outbreaks are damaging in the short term, McDonald’s swift containment efforts and safety measures may help restore confidence over time. With an extensive global presence, McDonald’s reputation for quick, affordable food will rely on its ability to manage crises like this effectively. Given the company’s scale and resources, experts believe McDonald’s has the tools necessary to resolve the outbreak efficiently and set a standard for food safety in the industry.
Conclusion
The McDonald’s E. coli outbreak presents a critical moment for both public health and corporate responsibility. While it has spurred immediate concern among consumers and investors alike, McDonald’s rapid response efforts may help limit the long-term impact. For other fast-food chains, this incident is a reminder of the importance of rigorous supply chain oversight, swift crisis management, and transparent communication. In the coming weeks, as McDonald’s works with health officials to identify the source and implement new safety measures, the company’s handling of the crisis will serve as a benchmark for food safety standards across the industry.